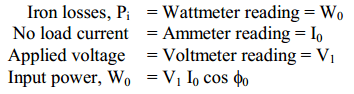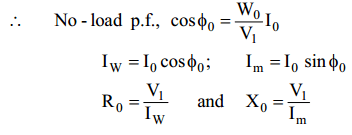Open Circuit & Short Circuit Tests on Transformers:
The circuit constants, efficiency and voltage regulation of a transformer can be determined by two simple tests:
(i) Open-circuit Test
(ii) Short-circuit Test
These tests are very convenient as they provide the required information without actually loading the transformer.Further, the power required to carry out these tests is very small as compared with the full-load output of the transformer. These tests consist of measuring the input voltage, current and power to the primary first with secondary open-circuited (open-circuit test) and then with the secondary short-circuited (short circuit test).
Open-Circuit or No-Load Test on Transformers:
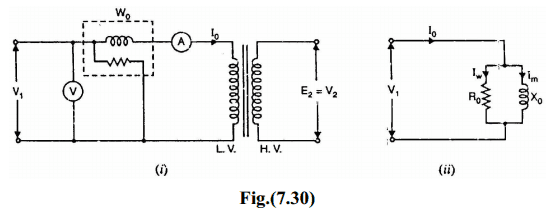
This test is conducted to determine the iron losses (or core losses) and parameters R0 and X0 of the transformer.In this test, the rated voltage is applied to the primary (usually low-voltage winding) while the secondary is left open circuited. The applied primary voltage V1 is measured by the voltmeter, the no load current I0 by an ammeter and no-load input power W0 by watt meter as shown in Fig. (7.30 (i)). As the normal rated voltage is applied to the primary, therefore, normal iron losses will occur in the transformer core.
Hence watt meter will record the iron losses and small copper loss in the primary. Since no-load current I0 is very small (usually 2-10 % of rated current). Cu losses in the primary under no-load condition are negligible as compared with iron losses. Hence, watt meter reading practically gives the iron losses in the transformer. It is reminded that iron losses are the same at all loads. Fig. (7.30 (ii)) shows the equivalent circuit of the transformer on no-load.
Thus open-circuit test enables us to determine iron losses and parameters R0 and X0 of the transformer.
Short-Circuit or Impedance Test on Transformers:
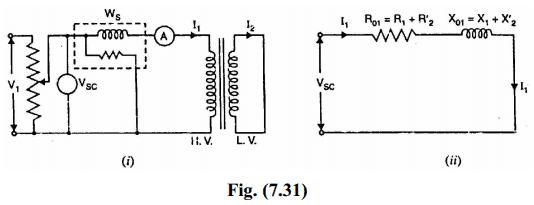
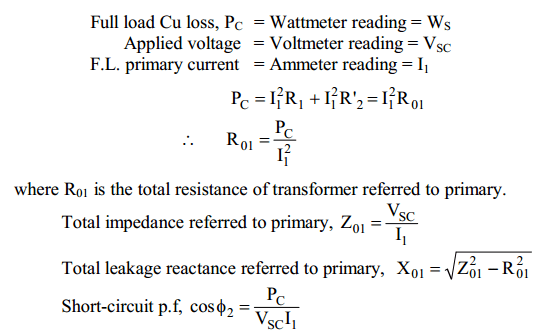
This test is conducted to determine R01 (or R02), X01 (or X02) and full-load copper losses of the transformer.In this test, the secondary (usually low-voltage winding) is short-circuited by a thick conductor and variable low voltage is applied to the primary as shown in Fig.(7.31 (i)).The low input voltage is gradually raised till at voltage Vsc, full-load current I1 flows in the primary.Then I2 in the secondary also has full-load value since I1/I2 = N2/N1. Under such conditions, the copper loss in the windings is the same as that on full load.
There is no output from the transformer under short-circuit conditions.Therefore, input power is all loss and this loss is almost entirely copper loss. It is because the iron loss in the core is negligibly small since the voltage VSC is very small. Hence, the wattmeter will practically register the full-load copper losses in the transformer windings.Fig. (7.31 (ii)) shows the equivalent circuit of a transformer on short circuit as referred to primary; the no-load current being neglected due to its smallness.
Thus short-circuit lest gives full-load Cu loss, R01 and X01.
Note: The short-circuit test will give full-load Cu loss only if the applied voltage Vsc is such so as to circulate full-load currents in the windings. If in a short circuit test, current value is other than full-load value, the Cu loss will be
corresponding to that current value.
Advantages of Tests performed on Transformers:
The above two simple transformer tests offer the following advantages:
(i) The power required to carry out these tests is very small as compared to the full-load output of the transformer. In case of open circuit lest, the power required is equal to the iron loss whereas, for a short-circuit test, the power required is equal to full-load copper loss.
(ii) These tests enable us to determine the efficiency of the transformer accurately at any load and p.f. without actually loading the transformer.
(iii) The short-circuit test enables us to determine R01 and X01 (or R02 and X02). We can thus find the total voltage drop in the transformer as referred to primary or secondary.This permits us to calculate voltage regulation of the transformer.