Circuit Breakers:
During the operation of power system, it is often desirable and necessary to switch on or off the various circuits (e.g., transmission lines, distributors, generating plants etc.) under both normal and abnormal conditions. In earlier days, this function used to be performed by a switch and a fuse placed in series with the circuit.However, such a means of control presents two disadvantages.Firstly, when a fuse blows out, it takes quite some time to replace it and restore supply to the customers.We are going to talk about circuit breakers.
Secondly, a fuse cannot successfully interrupt heavy fault currents that result from faults on modern high-voltage and large capacity circuits.Due to these disadvantages, the use of switches and fuses is limited to low-voltage and small capacity circuits where frequent operations are not expected e.g., for switching and protection of distribution transformers, lighting circuits, branch circuits of distribution lines etc.
With the advancement of the power system, the lines and other equipment operate at very high voltages and carry large currents.The arrangement of switches along with fuses cannot serve the desired function of switchgear in such high capacity circuits.This necessitates to employ a more dependable means of control such as is obtained by the use of circuit breakers.
A circuit breaker can make or break a circuit either manually or automatically under all conditions viz., no-load, full-load and short-circuit conditions.This characteristic of the circuit breaker has made it a very useful equipment for switching and protection of various parts of the power system.In this article, we shall deal with the various types of circuit breakers and their increasing applications as control devices.
A circuit breaker is a piece of equipment which can
(i) make or break a circuit either manually or by remote control under normal conditions
(ii) break a circuit automatically under fault conditions
(iii) make a circuit either manually or by remote control under fault conditions
Thus a circuit breaker incorporates manual (or remote control) as well as automatic control for switching functions.The latter control employs relays and operates only under fault conditions.
Working principle a circuit breaker:
A circuit breaker essentially consists of fixed and moving contacts, called electrodes.Under normal operating conditions, these contacts remain closed and will not open automatically until and unless the system becomes faulty.Of course, the contacts can be opened manually or by remote control whenever desired.When a fault occurs on any part of the system, the trip coils of the circuit breaker get energised and the moving contacts are pulled apart by some mechanism, thus opening the circuit.
When the contacts of a circuit breaker are separated under fault conditions, an arc is struck between them. The current is thus able to continue until the discharge ceases.The production of arc not only delays the current interruption process but it also generates enormous heat which may cause damage to the system or to the circuit breaker itself.Therefore, the main problem in a circuit breaker is to extinguish the arc within the shortest possible time so that heat generated by it may not reach a dangerous value.This is the basic working principle of circuit breaker.
Types of Circuit Breakers:
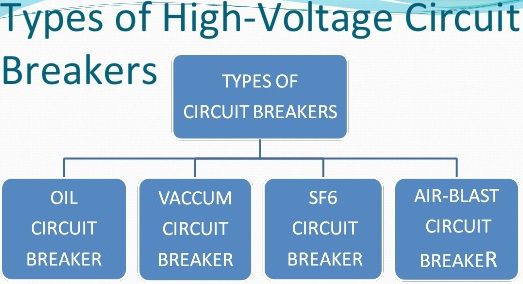
There are several ways of classifying the circuit breakers.There are many different types of circuit breakers on different basis.However, the most general way of classification is on the basis of medium used for arc extinction. The medium used for arc extinction is usually oil, air, sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) or vacuum.Accordingly, circuit breakers may be classified into :
(i) Oil circuit breakers which employ some insulating oil (e.g., transformer oil) for arc extinction.
(ii) Air-blast circuit breakers in which high pressure air-blast is used for extinguishing the arc.
(iii) Sulphur hexafluoride circuit breakers in which sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) gas is used for arc extinction.
(iv) Vacuum circuit breakers in which vacuum is used for arc extinction.
Secondly, depending on the voltage levels circuit breakers operate on there are three types of circuit breakers:
(i) Low Voltage Circuit Breakers
(ii) Medium Voltage Circuit Breakers
(iii) High Voltage Circuit Breakers
Based on the working principle of the circuit breaker, there are three types of circuit breakers:
(i) Hydraulic Circuit Breakers
(ii) Pneumatic Circuit Breakers
(iii) Spring actuated Circuit Breakers
Another very important classification depends on the usage of the circuit breaker.We must have to take care if it used inside your home or any other building or it has to be installed somewhere outdoors.This is because the mechanical body of the circuit breaker has to be designed accordingly or else the circuitry may get damage.There are two types of circuit breakers:
(i) Outdoor Circuit Breakers
(ii) Indoor Circuit Breakers