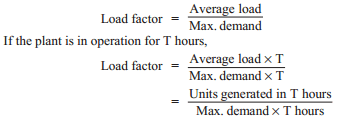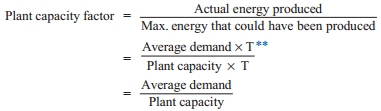Variable load on power stations:
Here I am going to explain you how the load connected to a power station is varied and what are terms used to describe the factors responsible for variable load.First of all, lets us know what is a variable load.Generally, in the house, we switch on lights, fan, TV and all other appliances only when we are at home.But when we are out of home all are switched off.So now the load is varied.Like this in every home, it happens and not only at home but many schools, hospitals, buildings, factories, offices.
The load on a power station varies from time to time due to uncertain demands of the consumers and is known as the variable load on the station.A power station is designed to meet the load requirements of the consumers.An ideal load on the station, from the stand point of equipment needed and operating routine, would be one of constant magnitude and steady duration.However, such a steady load on the station is never realised in actual practice.The consumers require their small or large block of power in accordance with the demands of their activities.Thus the load demand of one consumer at any time may be different from that of the other consumer.The result is that load on the power station varies from time to time.
Effects of variable load :
The variable load on a power station introduces many perplexities in its operation.Some of the important effects of variable load on a power station are :
(i) Need of additional equipment: The variable load on a power station necessitates to have additional equipment.By way of illustration, consider a steam power station.Air, coal and water are the raw materials for this plant. In order to produce variable power, the supply of these materials will be required to be varied correspondingly.
For instance, if the power demand on the plant increases, it must be followed by the increased flow of coal, air and water to the boiler in order to meet the increased demand.Therefore, additional equipment has to be installed to accomplish this job.As a matter of fact, in a modern power plant, there is much equipment devoted entirely to adjust the rates of supply of raw materials in accordance with the power demand made on the plant.
(ii) Increase in production cost: The variable load on the plant increases the cost of the production of electrical energy.An alternator operates at maximum efficiency near its rated capacity.If a single alternator is used, it will have poor efficiency during periods of light loads on the plant.
Therefore, in actual practice, a number of alternators of different capacities are installed so that most of the alternators can be operated at nearly full load capacity.However, the use of a number of generating units increases the initial cost per kW of the plant capacity as well as floor area required.This leads to the increase in production cost of energy.
Must Read:
Load Curves:
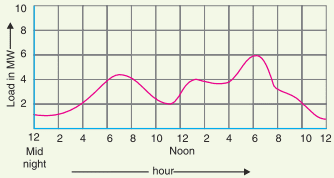
The curve showing the variation of load on the power station with respect to (w.r.t) time is known as a load curve.
The load on a power station is never constant; it varies from time to time.These load variations during the whole day (i.e., 24 hours) are recorded half-hourly or hourly and are plotted against time on the graph.The curve thus obtained is known as daily load curve as it shows the variations of load w.r.t. the time during the day.The figure below shows a typical daily load curve of a power station.It is clear that load on the power station is varying, being maximum at 6 P.M. in this case.It may be seen that load curve indicates at a glance the general character of the load that is being imposed on the plant.Such a clear representation cannot be obtained from tabulated figures.The monthly load curve can be obtained from the daily load curves of that month.For this purpose, average values of power over a month at different times of the day are calculated and then plotted on the graph.The monthly load curve is generally used to fix the rates of energy.The yearly load curve is obtained by considering the monthly load curves of that particular year.The yearly load curve is generally used to determine the annual load factor.
Importance: The daily load curves have attained a great importance in a generation as they supply the following information readily :
(i) The daily load curve shows the variations of load on the power station during different hours of the day.
(ii)The area under the daily load curve gives the number of units generated in the day.
Units generated/day = Area (in kWh) under daily load curve.
(iii)The highest point on the daily load curve represents the maximum demand on the station on that day.
(iv) The area under the daily load curve divided by the total number of hours gives the average load on the station in the day.
Average load =Area (in kWh) under daily load curve/24hours
(v)The ratio of the area under the load curve to the total area of a rectangle in which it is contained gives the load factor.
Load factor=Average load/Max. demand=Average load × 24/Max. demand ×24=Area (in kWh) under daily load curve/Total area of a rectangle in which the load curve is contained.
(vi)The load curve helps in selecting the size and number of generating units.
(vii)The load curve helps in preparing the operation schedule of the station.
Important terms and factors:
The variable load problem has introduced the following terms and factors in power plant engineering:
(i) Connected load: It is the sum of continuous ratings of all the equipment connected to supply system.A power station supplies load to thousands of consumers.Each consumer has certain equipment installed in his premises. The sum of the continuous ratings of all the equipment in the consumer’s premises is the “connected load” of the consumer.
For instance, if a consumer has connections of five 100-watt lamps and a power point of 500 watts, then connected load of the consumer is 5 × 100 + 500 = 1000 watts.The sum of the connected loads of all the consumers is the connected load to the power station.
(ii) Maximum demand: It is the greatest demand of load on the power station during a given period.The load on the power station varies from time to time.The maximum of all the demands that have occurred during a given period (say a day) is the maximum demand.Thus referring back to the load curve of Figure below the maximum demand on the power station during the day is 6 MW and it occurs at 6 P.M.
Maximum demand is generally less than the connected load because all the consumers do not switch on their connected load to the system at a time.The knowledge of maximum demand is very important as it helps in determining the installed capacity of the station.The station must be capable of meeting the maximum demand.
(iii) Demand factor: It is the ratio of maximum demand on the power station to its connected load i.e.,
Demand factor = Maximum demand/Connected load
The value of demand factor is usually less than 1.It is expected because maximum demand on the power station is generally less than the connected load.If the maximum demand on the power station is 80 MW and the connected load is 100 MW, then demand factor = 80/100 = 0·8.The knowledge of demand factor is vital in determining the capacity of the plant equipment.
(iv) Average load: The average of loads occurring on the power station in a given period (day or month or year) is known as average load or average demand.
(v) Load factor: The ratio of average load to the maximum demand during a given period is known as load factor i.e.,
The load factor may be daily load factor, monthly load factor or annual load factor if the time period considered is a day or month or year.Load factor is always less than 1 because the average load is smaller than the maximum demand.The load factor plays a key role in determining the overall cost per unit generated. Higher the load factor of the power station, lesser will be the cost per unit generated.
(vi) Diversity factor: The ratio of the sum of individual maximum demands to the maximum demand on power station is known as diversity factor i.e.,
A power station supplies load to various types of consumers whose maximum demands generally do not occur at the same time.Therefore, the maximum demand on the power station is always less than the sum of individual maximum demands of the consumers.Obviously, diversity factor will always be greater than 1.The greater the diversity factor, the lesser is the cost of generation of power.
(vii) Plant capacity factor: It is the ratio of actual energy produced to the maximum possible energy that could have been produced during a given period i.e.,
Thus if the considered period is one year,
The plant capacity factor is an indication of the reserve capacity of the plant. A power station is so designed that it has some reserve capacity for meeting the increased load demand in future.Therefore, the installed capacity of the plant is always somewhat greater than the maximum demand on the plant.
Reserve Capacity = Plant capacity − Max. demand
It is interesting to note that difference between load factor and plant capacity factor is an indication of reserve capacity.If the maximum demand on the plant is equal to the plant capacity, then load factor and plant capacity factor will have the same value.In such a case, the plant will have no reserve capacity.
(viii) Plant use factor: It is ratio of kWh generated to the product of plant capacity and the number of hours for which the plant was in operation i.e.
Must Read:
Load duration curve:
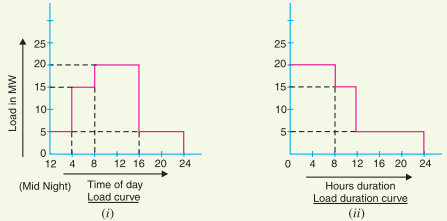
When the load elements of a load curve are arranged in the order of descending magnitudes, the curve thus obtained is called a load duration curve.The load duration curve is obtained from the same data as the load curve but the ordinates are arranged in the order of descending magnitudes. In other words, the maximum load is represented to the left and decreasing loads are represented to the right in the descending order.
Hence the area under the load duration curve and the area under the load curve are equal.The figure below shows the daily load curve.The daily load duration curve can be readily obtained from it.It is clear from daily load curve, those load elements in order of descending magnitude are 20 MW for 8 hours; 15 MW for 4 hours and 5 MW for 12 hours.Plotting these loads in order of descending magnitude, we get the daily load duration curve as shown in Figure below.
The following points may be noted about load duration curve :
(i) The load duration curve gives the data in a more presentable form. In other words, it readily shows the number of hours during which the given load has prevailed.
(ii)The area under the load duration curve is equal to that of the corresponding load curve. Obviously, the area under daily load duration curve (in kWh) will give the units generated on that day.
(iii) The load duration curve can be extended to include any period of time. By laying out the abscissa from 0 hours to 8760 hours, the variation and distribution of demand for an entire year can be summarised in one curve. The curve thus obtained is called the annual load duration curve.
Types of loads:
A device which taps electrical energy from the electric power system is called a load on the system.The load may be resistive (e.g., electric lamp), inductive (e.g., induction motor), capacitive or some combination of them. The various types of loads on the power system are :
(i) Domestic load: Domestic load consists of lights, fans, refrigerators, heaters, television, small motors for pumping water etc.Most of the residential load occurs only for some hours during the day (i.e., 24 hours) e.g., lighting load occurs during night time and domestic appliance load occurs for only a few hours. For this reason, the load factor is low (10% to 12%).
(ii) Commercial load : This type of load consists of lighting for shops, fans and electric appliances used in restaurants etc. This class of load occurs for more hours during the day as compared to the domestic load. The commercial load has seasonal variations due to the extensive use of air conditioners and space heaters.
(iii) Industrial load : Industrial load consists of load demand by industries. The magnitude of industrial load depends upon the type of industry.Thus small scale industry requires load upto 25 kW, medium scale industry between 25kW and 100 kW and large-scale industry requires load above 500 kW. Industrial loads are generally not weather dependent.
(iv) Municipal load : Municipal load consists of street lighting, power required for water supply and drainage purposes.Street lighting load is practically constant throughout the hours of the night.For water supply, water is pumped to overhead tanks by pumps driven by electric motors.Pumping is carried out during the off-peak period, usually occurring during the night.This helps to improve the load factor of the power system.
(v) Irrigation load : This type of load is the electric power needed for pumps driven by motors to supply water to fields.Generally this type of load is supplied for 12 hours during night.
(vi) Traction load : This type of load includes tram cars, trolley buses, railways etc.This class of load has wide variation.During the morning hour, it reaches peak value because people have to go to their work place.After morning hours, the load starts decreasing and again rises during evening
since the people start coming to their homes.